AI Taxonomy

Good day, I’m Mark Heather. After spending the past year immersed in generative AI, I’ve noticed that its rapid advancement is making things incomprehensible for those of us that don’t speak “AI geek.” So, although the following may not be an exact definition of terms, it’s an attempt to translate AI Geek into plain English so that we mortals can grasp the quantum leaps AI is making in terms of business, corporate structures, and capability.
General Statements:
- AI is NOT a computer program: You will not get the same answer twice when asking a question. AI is like interacting with a human. If you ask two humans the same question, you will get two slightly different answers. Both can be correct, but there are slight differences depending on their experiences. AI acts like a human; it has understanding.
- AI uses models programmed with prompts: So, instead of computer programmers, we have prompt engineers, and instead of programs, we have models.
- AI has agents: An AI agent is an autonomous entity that uses AI models to interact with its environment and achieve goals.
GPT Versions: Why are there different versions and what has been the reason?
- GPT-3.5: The first widely used version of Chat GPT, released in December 2022, is a text-to-text model with strong output capabilities. However, it was prone to hallucinations that occasionally gave inaccurate responses. It could produce reports about 1-2 pages of A4 in length.
- GPT-4: Introduced in March 2023, GPT-4 added multimodal capabilities with enhanced text, image, and audio processing. It is more accurate and less prone to hallucinations, still producing reports of about 1-2 pages of A4.
- GPT-4o: Released in May 2024, GPT-4o is faster, more cost-effective, and offers multilingual support. It gives improved performance in non-English languages. Its multimedia capabilities include handling vision and audio tasks with enhanced accuracy. GPT-4o can produce reports in excess of 10 pages of A4 in length.
The key enhancements with each release focus on improved reasoning and accuracy:
- GPT-3.5 has reasoning and accuracy at the level of a high school graduate.
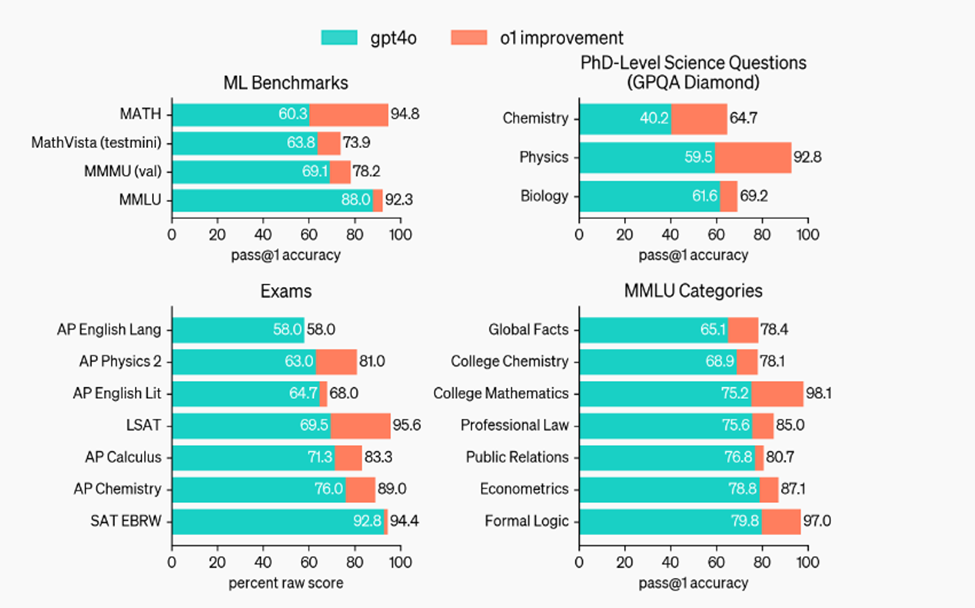
- The latest LLM from OpenAI, GPT-o1 Preview, operates at the level of a university graduate with a PhD.
This has all happened in under 2 years.
OpenAI’s “Strawberry” Model (OpenAI o1):
OpenAI’s "Strawberry" model, or OpenAI o1, represents a major step forward in AI technology, focusing on enhanced reasoning and problem-solving. It offers improved accuracy, versatility, and cost-effective options, making it a powerful tool for a wide range of applications.
Single Agent vs Collaborative Multi-Agent Systems:
- Single Agent Systems: Most AI systems use a single-agent approach to carry out a particular task. They may have multiple single agents, but these agents do not communicate with each other. Examples include web crawlers, chatbots, and monitoring systems.
- Collaborative Agents: These work together, sharing information and coordinating actions to achieve common goals. Examples include autonomous vehicles, smart home systems, and healthcare diagnostics.
Questions to Ask Vendors Claiming AI:
When vendors claim to have AI in their products, how can we distinguish how they are using AI and what benefits it provides? To differentiate, ask the following questions:
- What level of reasoning and understanding does your AI demonstrate—comparable to a high school graduate, university graduate, or higher? How does your AI handle reasoning and problem-solving tasks? Does it perform basic logical reasoning (Level-1) or advanced analytical thinking (Level-2)? Please provide definitions for these levels as they apply to your AI.
- Is your AI system based on single-agent or collaborative multi-agent architectures?
- Does your AI system perform iterative reasoning or multi-step problem-solving? What are the limitations on processing time or the number of reasoning steps?
- Does your AI have multimodal capabilities, such as processing text, images, and audio?
- How does your AI system ensure data privacy and security for users?